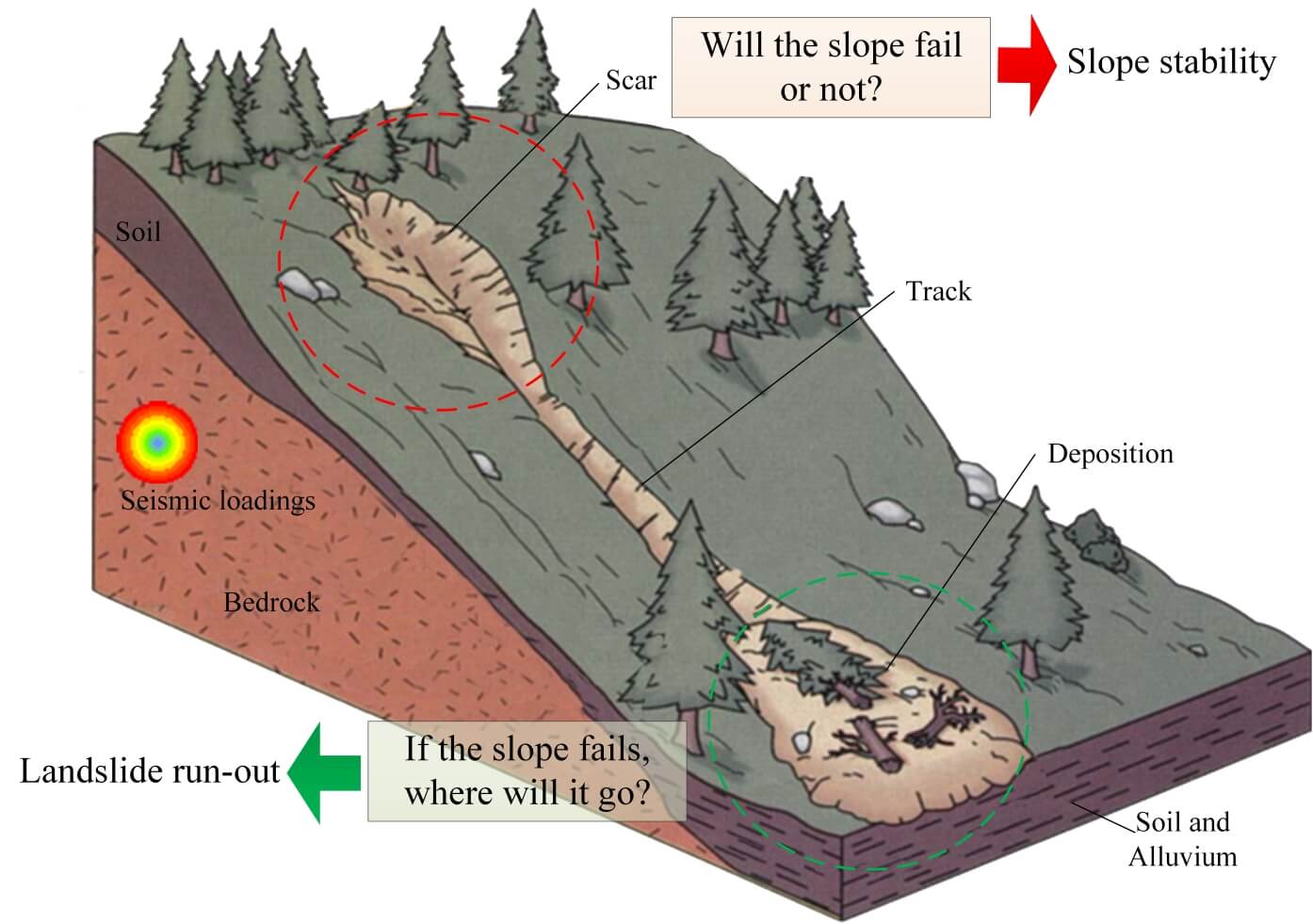
Stability and Runout Analysis of Earthquakeinduced Landslides IntechOpen
The calculation of the safety of a sliding block on a plane (a layered slide with preferential failure along pre-existing weaknesses) is shown below in figure 1. This calculation takes into account slope angle, friction, cohesion, and water content. Increasing water content and slope angle decreases the factor of safety.
Landslides
ENCYCLOPEDIC ENTRY Landslide A landslide is the movement of rock, earth, or debris down a sloped section of land. Grades 6 - 12+ Subjects Earth Science, Geology, Geography, Human Geography, Physical Geography Photograph Proof of a Landslide
Landslide As Mountain or Cliff Collapse Geological Structure Outline Diagram Stock Vector
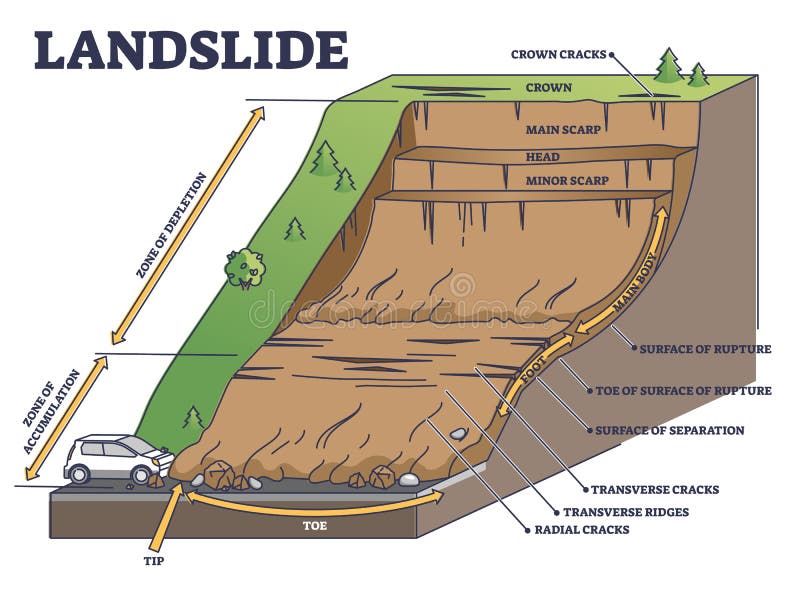
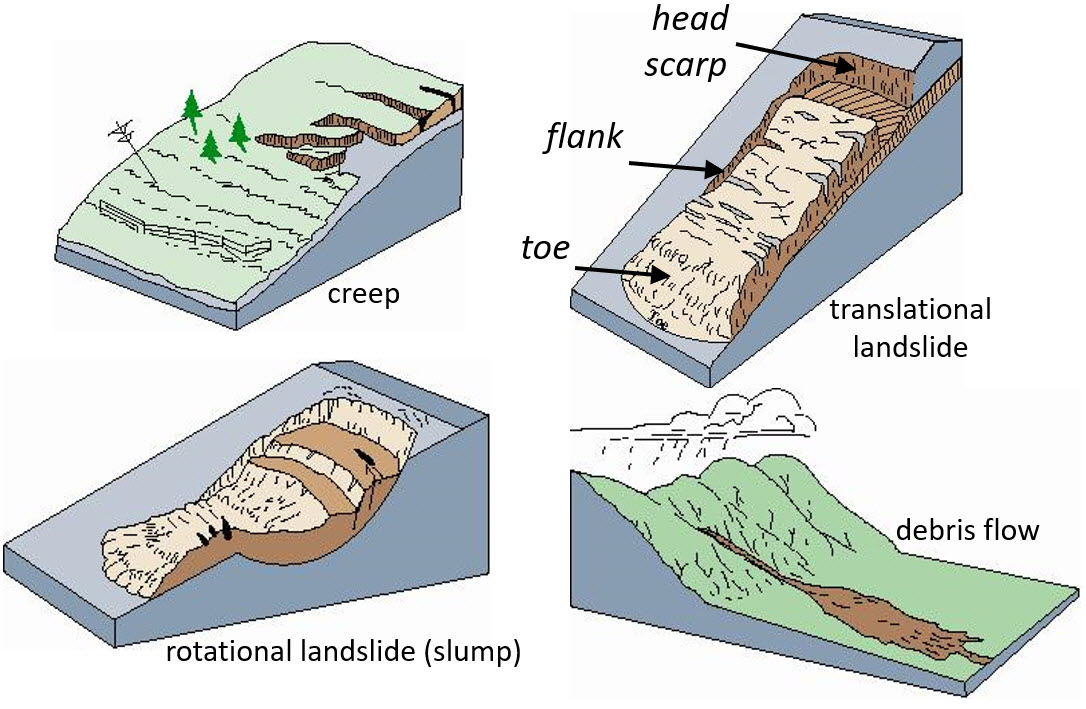
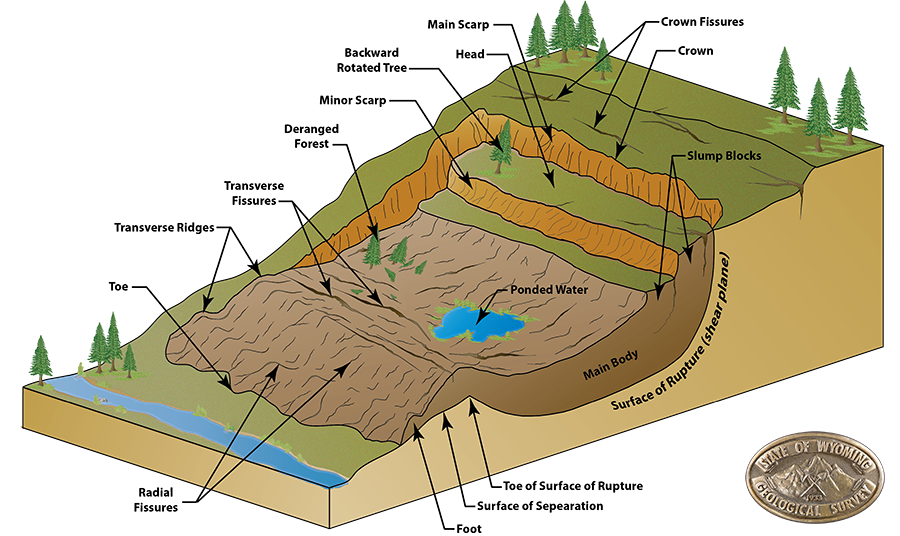
Diagram of a rotational landslide. Parts Description; Crown: The undisturbed material uphill of the scarp. (i.e. the brown house at the top of the hill) Main Scarp: Steep slope at the upper edge of the landslide (at the head), caused by the movement of displaced material away from the undisturbed ground. The visible part of the slide surface.

Active landslide geomorphic evolution and deepseated landslide... Download Scientific Diagram
Lesson 8: Landslides Hazards. Earthquakes are a major cause of landslides. Landslides occur when masses of rock, earth material, or debris flows move down a slope due to gravity. Landslides can.

Mass Movement Geography
This diagrams also reflects conditions of geology surrounding Vaiont Dam. If people dig into the base of a slope to create a road or a homesite, the slope may become unstable and move downhill. This is particularly dangerous when the underlying rock layers slope towards the area.

UGS Landslide Illustrations by Jeremy Gleason at
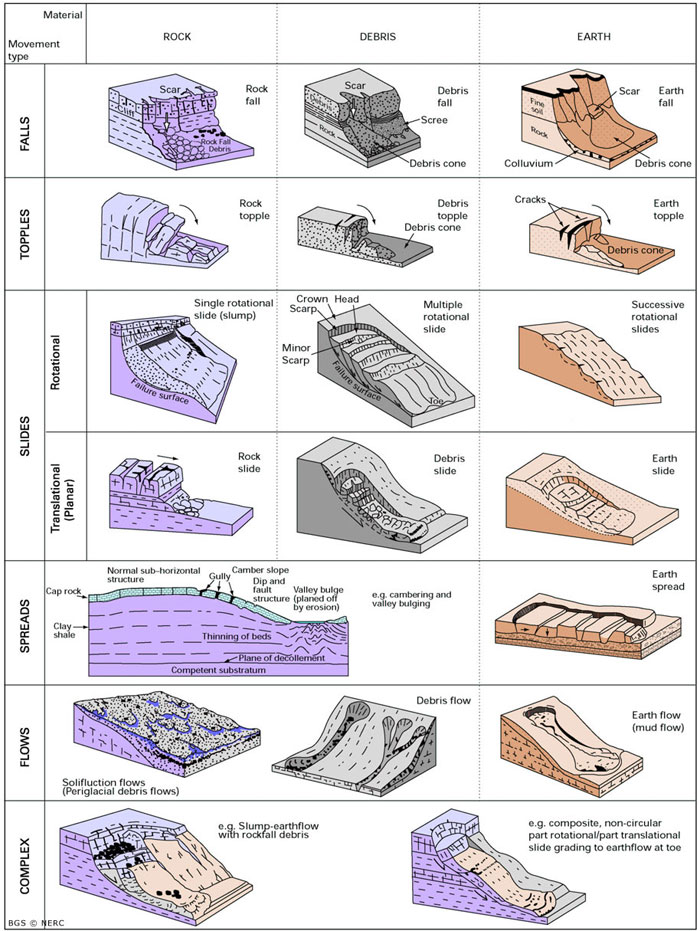
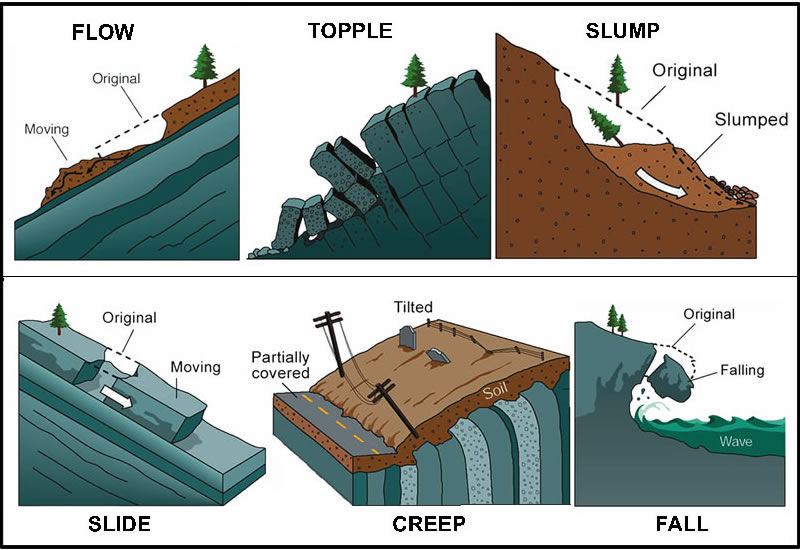
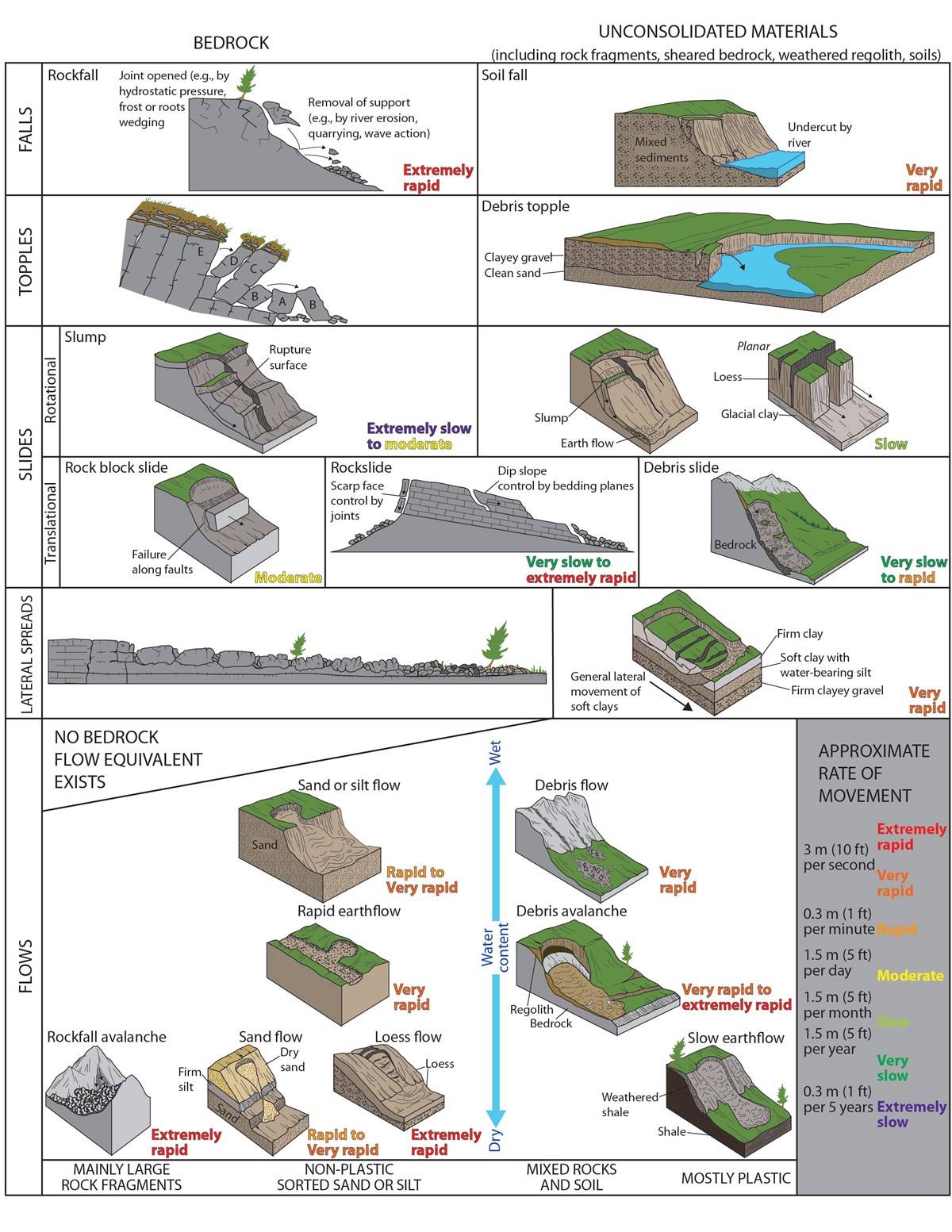
The term "landslide" describes a wide variety of processes that result in the downward and outward movement of slope-forming materials including rock, soil, artificial fill, or a com-bination of these. The materials may move by falling, toppling, sliding, spreading, or flowing.

Block diagram of a typical landslide and its component (USGS, 2009) Download Scientific Diagram
A landslide is defined as the movement of a mass of rock, debris, or earth down a slope. Landslides are a type of "mass wasting," which denotes any down-slope movement of soil and rock under the direct influence of gravity. The term "landslide" encompasses five modes of slope movement: falls, topples, slides, spreads, and flows.
Landslide Information help file
The term "landslide" describes a wide variety of processes that result in the downward and outward movement of slope-forming materials including rock, soil, artificial fill, or a combination of these. The materials may move by falling, toppling, sliding, spreading, or flowing.

5 Examples of landslide mechanisms and mass wasting processes... Download Scientific Diagram
Slides. Figure 3. These schematics illustrate the major types of landslide movement. Although many types of mass movements are included in the general term "landslide," the more restrictive use of the term refers only to mass movements, where there is a distinct zone of weakness that separates the slide material from more stable underlying material.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/rockfall-5b7ae564c9e77c002502137a.jpg)
Different Forms and Sizes of Landslides Gallery
Includes diagrams of different landslide types. The Landslides Handbook- A Guide to Understanding Landslides (Handbook), U.S. Geological Survey This comprehensive resource for a lay audience includes detailed information on types of landslides, where landslides occur, landslide causes, and landslide effects/consequences.

Idaho Geological Survey Landslides
What is a landslide? A landslide is a mass movement of material, such as rock, earth or debris, down a slope. They can happen suddenly or more slowly over long periods of time. When the force of gravity acting on a slope exceeds the resisting forces of a slope, the slope will fail and a landslide occurs.
The Haverstraw Landslide Feb. 1, 2018 The Catskill Geologist
The term "landslide" describes a wide variety of processes that result in the downward and outward movement of slope-forming materials including rock, soil, artificial fill, or a combination of these. The materials may move by falling, toppling, sliding, spreading, or flowing.

This graphic illustrates commonlyused labels for the parts of a... Download Scientific Diagram
Landslides are a form of mass movement, a term used to describe any sort of gravity-induced movement of sediment down a slope. Mass movements can occur slowly over a period of years, or they can happen in a matter of minutes.
Earth’s Forces ETEAMS
Therefore, α1α2α3 = 1 and β1 + β2 + β3 = 1. For graphical data presentation, β1, β2, β3 are the tools for interpreting the landslide geometry. The ternary diagram shown in Fig. 10 clearly demonstrates the differences between the three landslides observed. SL have smaller L , W, and H, and similar average β1 and β2.
Landslide Hazards Geohazards (U.S. National Park Service)
The causes of landslides are usually related to instabilities in slopes. It is usually possible to identify one or more landslide causes and one landslide trigger. The difference between these two concepts is subtle but important.. the mechanics are essentially as per a real landslide. A: Diagram illustrating the resistance to, and causes of
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Slumping-5b7ae18446e0fb002c2f530c.jpg)
Different Forms and Sizes of Landslides Gallery
Learn what a landslide is by exploring different types of landslides, what causes a landslide, the impact of landslides, and seeing a diagram of a landslide. Updated: 11/21/2023 Table of.